#Multimodal Innovation and AI-Based Mobile Apps
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text

Based on the search results, here are some innovative technologies that RideBoom could implement to enhance the user experience and stay ahead of ONDC:
Enhanced Safety Measures: RideBoom has already implemented additional safety measures, including enhanced driver background checks, real-time trip monitoring, and improved emergency response protocols. [1] To stay ahead, they could further enhance safety by integrating advanced telematics and AI-powered driver monitoring systems to ensure safe driving behavior.
Personalized and Customizable Services: RideBoom could introduce a more personalized user experience by leveraging data analytics and machine learning to understand individual preferences and offer tailored services. This could include features like customizable ride preferences, personalized recommendations, and the ability to save preferred routes or driver profiles. [1]
Seamless Multimodal Integration: To provide a more comprehensive transportation solution, RideBoom could integrate with other modes of transportation, such as public transit, bike-sharing, or micro-mobility options. This would allow users to plan and book their entire journey seamlessly through the RideBoom app, enhancing the overall user experience. [1]
Sustainable and Eco-friendly Initiatives: RideBoom has already started introducing electric and hybrid vehicles to its fleet, but they could further expand their green initiatives. This could include offering incentives for eco-friendly ride choices, partnering with renewable energy providers, and implementing carbon offset programs to reduce the environmental impact of their operations. [1]
Innovative Payment and Loyalty Solutions: To stay competitive with ONDC's zero-commission model, RideBoom could explore innovative payment options, such as integrated digital wallets, subscription-based services, or loyalty programs that offer rewards and discounts to frequent users. This could help attract and retain customers by providing more value-added services. [2]
Robust Data Analytics and Predictive Capabilities: RideBoom could leverage advanced data analytics and predictive modeling to optimize their operations, anticipate demand patterns, and proactively address user needs. This could include features like dynamic pricing, intelligent routing, and personalized recommendations to enhance the overall user experience. [1]
By implementing these innovative technologies, RideBoom can differentiate itself from ONDC, provide a more seamless and personalized user experience, and stay ahead of the competition in the on-demand transportation market.
#rideboom#rideboom app#delhi rideboom#ola cabs#biketaxi#uber#rideboom taxi app#ola#uber driver#uber taxi#rideboomindia#rideboom uber
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Introduce Gemma 3n preview, Veo 3, Imagen 4 & Veo 2 updates

New Google AI Models and Tools Advance Creative Media Creation and On-Device AI
Google has announced numerous new models and tools that emphasise advanced generative media production and on-device capabilities to make AI more accessible.
Gemma 3n
Gemma 3n preview, a powerful, mobile-first AI model, is important. Gemma 3n, the first open model with a new architecture, was developed with Qualcomm Technologies, MediaTek, and Samsung System LSI. This architecture is optimised for rapid, multimodal AI to enable truly private and intimate interactions on computers, tablets, and phones.
Gemma 3n's main features:
Compared to Gemma 3 4B, it reacts 1.5 times faster on mobile devices, has better quality, and uses less memory. Per-Layer Embeddings (PLE) reduces RAM usage and allows models with 5B and 8B parameter counts to work with a dynamic memory footprint of ONLY 2GB and 3GB.
MatFormer training allows a 4B active memory footprint model to natively incorporate a layered state-of-the-art 2B active memory footprint submodel. This lets you dynamically balance quality and performance. We add mix-and-match capability to the 4B model to dynamically construct submodels for certain use scenarios.
Privacy-First & Offline Ready: Local execution enables features that safeguard user privacy and work offline.
Gemma 3n understands text, sounds, and visuals well and has excellent video understanding. Audio features include high-quality Automatic Speech Recognition and Translation. Accepting interleaved data from multiple modalities lets it understand complex relationships.
It performs better overall, but best in Japanese, German, Korean, Spanish, and French.
Gemma 3n gives an early peek at Android and Chrome's architectural breakthroughs with the Gemini Nano generation, which will be powered by this same architecture and released later this year. Google AI Edge for on-device development and Google AI Studio for cloud-based research allow developers to preview Gemma 3n today.
Google is releasing new generative media tools and models in addition to on-device improvements. These aim to empower artists and producers by pushing media generation.
The updated and new creative tools are:
Veo 3: A revolutionary video-making model that records speech, traffic, and bird sounds. It works in text and image prompting, lip syncing, and physics. Enterprise users can use Veo 3 on Vertex AI, while US Ultra subscribers can use Gemini and Flow.
Veo 2 updates: Creator feedback led to object add/remove capability, camera controls for precise movements, outpainting to extend the frame, and state-of-the-art reference-powered video for creative control and consistency. Flow has reference-powered camera and video controllers.
Flow: A Veo-specific AI filmmaking tool for creatives. Flow lets users create cinematic scenes, clips, and narratives using Google DeepMind's most advanced models (Veo, Imagen, and Gemini). Users can describe photos in plain language and manage plot elements. Google AI Pro and Ultra US subscribers can now use Flow.
Imagen 4, the latest model, produces gorgeous images with great typography quickly and accurately. Imagen 4 supports aspect ratios up to 2k, has enhanced typeface and spelling, has excellent detail clarity, and works well in many styles. The Gemini app, Whisk, and Vertex AI offer it with Workspace apps like Slides, Vids, and Docs. A faster version is coming.
Lyria 2: This music creation paradigm now allows unlimited research and innovation. Businesses may employ Vertex AI and creators can use Lyria 2. AI Studio and API access MusicFX DJ's interactive music composition model, Lyria RealTime.
Google emphasises responsible AI development. SynthID watermarks will help identify Veo 3, Imagen 4, and Lyria 2 outputs as AI-generated. This watermark-based verification gateway, SynthID Detector, is unveiled today to help consumers recognise AI-generated content. As AI advances, Google is apprehensive of open models and strives to enhance protocols. It aims to unleash creativity and help creators realise their ideas.
#Gemma3n#Gemma3npreview#Imagen4#Veo3#Lyria2#Veo2updates#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Smart Transportation Market Trends to 2032: Size, Share, Scope, Growth & Industry Forecast
The smart transportation market is experiencing rapid transformation, driven by advancements in technology, urbanization, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and efficiency. As cities become more congested and populations continue to rise, governments and private sector players are embracing smart mobility solutions to improve traffic flow, reduce environmental impact, and enhance overall commuter experience. From connected vehicles to intelligent traffic systems, the future of transportation is becoming increasingly digital, data-driven, and automated.
The smart transportation market is not just evolving; it is revolutionizing the way we think about mobility. With the integration of Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Big Data, transportation systems are becoming more adaptive and predictive. These technologies are enabling real-time monitoring, automated traffic control, and seamless multimodal commuting. As both public and private sectors invest heavily in infrastructure and innovation, the global market is set for sustained growth over the coming years.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/1015
Market Keyplayers:
Siemens Mobility – Sitraffic Traffic Management System
Thales Group – SelTrac CBTC (Communication-Based Train Control)
Cubic Corporation – NextBus Real-Time Passenger Information System
Alstom – Urbalis 400 CBTC System
IBM Corporation – IBM Intelligent Operations Center
Cisco Systems, Inc. – Cisco Connected Roadways
Hitachi Rail – Lumada Intelligent Mobility Management
Kapsch TrafficCom – EcoTrafiX Traffic Management Suite
TomTom International BV – TomTom Traffic
Indra Sistemas – Horus Traffic Management System
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. – Huawei Smart Urban Transportation Solution
GE Transportation (Wabtec Corporation) – Trip Optimizer
TransCore – TransSuite Traffic Management System
Trends
Several key trends are shaping the smart transportation industry, each contributing to its expansion and modernization:
Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAVs): The development of self-driving and connected vehicles is accelerating. These vehicles communicate with each other and with smart infrastructure to ensure safer and more efficient travel.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS): Consumers are shifting from vehicle ownership to on-demand transportation models. Apps offering integrated mobility services—combining buses, trains, rideshares, and bikes—are on the rise.
Smart Traffic Management Systems: AI-powered traffic signals and sensors are optimizing traffic flow, reducing congestion, and improving emergency response times.
Electrification of Transportation: The push for sustainability is leading to widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the development of smart EV charging networks.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Big data analytics is helping urban planners and authorities understand travel patterns, reduce bottlenecks, and improve infrastructure planning.
Enquiry of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/enquiry/1015
Market Segmentation:
By Solution
Ticketing Management System
Parking Management System
Integrated Supervision System
Traffic Management System
By Service
Cloud Services
Business Services
Professional Services
Analysis
North America and Europe are leading the adoption of smart transportation technologies, thanks to well-established infrastructure and early investments. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like China and India, is quickly catching up due to massive urbanization projects and government-backed smart city programs. The Middle East is also emerging as a smart mobility hub, with ambitious projects in cities like Dubai and Riyadh.
Despite promising growth, the market does face challenges such as high implementation costs, regulatory hurdles, data privacy concerns, and interoperability between different systems and technologies. Still, continued collaboration between governments, tech companies, and automotive manufacturers is helping to address these issues.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the smart transportation market holds immense potential for innovation and expansion. As 5G networks roll out globally, real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure will become more reliable and efficient, enhancing safety and automation capabilities.
Smart public transportation systems are also expected to evolve, with AI managing everything from scheduling and route optimization to predictive maintenance. Urban air mobility, including drones and flying taxis, is no longer just a futuristic idea—it is progressing through development and pilot testing phases in multiple regions.
Additionally, the integration of blockchain for secure ticketing, payment systems, and data sharing will enhance transparency and trust in mobility services. Environmental sustainability will remain at the forefront, with further innovations in electric mobility, shared transportation, and green infrastructure paving the way for low-emission smart cities.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/smart-transportation-market-1015
Conclusion
The smart transportation market is set to redefine global mobility. With the convergence of AI, IoT, cloud computing, and big data, transportation is becoming safer, faster, cleaner, and more user-centric. Governments, businesses, and consumers alike are recognizing the importance of smart mobility in building more sustainable and efficient cities.
As the industry overcomes current challenges and continues to embrace innovation, the future of transportation looks intelligent, interconnected, and inclusive. The rapid growth of the smart transportation market is not just a technological shift—it’s a movement towards a smarter, more sustainable future.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
0 notes
Text
When Should You Choose Local vs. Cloud-Based DCM Viewers? A Comparison Guide
To inspect these datasets, a specialized "DCM viewer" is required. When selecting software, two key options exist:
Local viewers run directly on hospital workstations or personal devices. Cloud-based viewers instead utilize centralized, web-deployed infrastructure, allowing remote access.
But which architecture makes the most sense for your use case? In this guide, we'll compare local and cloud DCM viewers across critical factors like security, speed, mobility, pricing, and more.
Decide what's most important for your workflow to choose the optimal approach.
Local Viewer Benefits
Installing viewing software natively on individual devices offers these advantages:
1. Speed And Responsiveness
With local storage, transfer times are minimized. Images are immediately available to indexing processes that enable instantaneous rendering and manipulation.
Cloud latency from pipes or caching delays perception, especially for blazing-fast interactions like:
Rapid review/comparison of high-res multimodal scans and linked priors
Quickly paging through frame-by-frame ultrasound video
Modifying 3D opacity transfer functions on the fly
If snappy performance is mandatory, avoid roundtrips to cloud servers, which downgrade interactivity.
2. Security And Privacy
No transmission means no interception. Keeping protected health information (PHI) inside hospital networks with verified security protocols prevents breaches during transfer or cloud retention. Compliance is simplified.
While reputable providers offer robust cloud protection, local storage guarantees safety for sensitive clinical data or patient-identifiable scans used in teaching. Some institutions have policies prohibiting cloud usage entirely.
3. Reliability And Uptime
Once configured, local setups have essentially 100% guaranteed availability, unaffected by Internet connectivity problems. Cloud services rely on always-on links without disruption. Temporary ISP or infrastructure issues can cut access and halt diagnoses if servers can’t be reached.
For this reason, many clinicians maintain local mirrors with cloud backup rather than relying solely on cloud continuity. Redundancy is key for mission-critical diagnosis.
4. Granular Control
When managing your own infrastructure, software customizations, integration with other hospital IT systems, and long-term retention rules are easier to tailor to your needs. Change requests don’t require vendor submission/approval. You own the servers, desktop clients, and everything in between.
If your workflows demand unique handling, modification freedom makes local more convenient than conforming usage to external cloud restrictions.
Cloud Viewer Benefits
Alternatively, cloud-hosted remote DCM viewers offer their own compelling advantages:
1. Lower Upfront Cost
Delivering apps and storage from centralized data centers allows massive economies of scale, reducing per-user pricing.
For budget-limited practices, cloud subscriptions are far cheaper than investing in compliant on-premise hardware like medical workstations, servers, and backup systems.
Ongoing fees are also lower since hardware administration and life-cycling costs are eliminated. Patching, maintenance, expansions, and tech payroll to manage infrastructure all become provider responsibilities you’re relieved from.
2. Advanced Capabilities
Top-tier SaaS vendors dedicate enormous R&D budgets towards continually expanding and refining AI-enhanced features. The scope of innovation easily surpasses in-house efforts for all but the largest hospital chains:
Automated findings tagging and indexing
Contextual priors suggestion during interpretation
Real-time quality checking to prevent errors
Predictive analytics revealing trends
Accessing cutting-edge tools this way frees up your own resources to focus on patients rather than platform development.
3. Seamless Collaboration
Cloud sharing simplifies coordinating diagnosis and second opinions between staffers, external specialists, and partner sites. Cases are instantly accessible anywhere via links instead of requiring local transfer or VPN access.
Multi-party videoconferencing can reference scans in real time during virtual rounds. Annotations highlight areas of concern and are preserved with studies.
4. Superior Reliability
Leading SaaS providers deliver guaranteed 99.99% or better uptime via resilient server farms with automatic failover. Studying continuity statistics reveals most downtime is planned maintenance or minor blips, avoiding doctors' dependence on institutional infrastructure they can’t fully trust.
Natural disasters that might damage localized servers won’t interrupt globally distributed cloud access. For clinicians at smaller clinics, reliability should be weighed heavily.
5. Enhanced Mobility
Cloud liberates diagnosticians from confined workstation locations. As long as Internet access exists on laptops, tablets, or even phones, caseloads are reachable anywhere via browsers or apps.
Better portability aids quicker turnaround times, allows off-site analysis, improves home flexibility, and enables bringing imaging to patients’ bedsides.
Key Decision Factors
Now that we’ve surveyed the advantages in both directions, determining optimal DCM viewer deployment depends on your unique requirements. Here are key considerations:
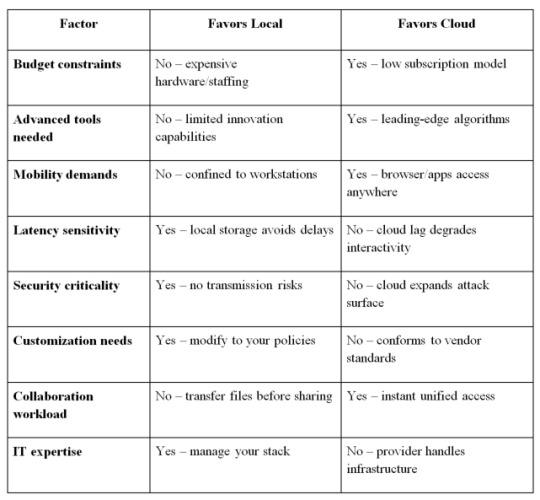
Beyond the table above, also decide if you need a universal viewer able to handle all modalities or more specialized DCM software dedicated to certain scenarios like cardiology or dental. Mixing multiple solutions is common to serve different use cases.
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is a complex file standard used globally to store medical images and related data.
0 notes
Text
Future Tech Trends in Taxi App Development
In the ever-evolving landscape of transportation and mobility, taxi app technology has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the way people access and experience transportation services. As consumer demands and technological advancements continue to shape the industry, the future of taxi app technology is poised to bring about significant transformations that will redefine convenience, efficiency, and user experience.
The Rise of Ride-Hailing Apps
The advent of ride-hailing apps like Uber and Lyft has disrupted the traditional taxi industry, introducing a new era of on-demand transportation services. According to a report by Statista, the global ride-hailing market is expected to reach $344 billion by 2030, underscoring the immense growth potential of this sector. As these platforms continue to gain traction, the demand for innovative and user-friendly taxi app technology will soar.
Emerging Trends in Taxi App Technology
White Label Taxi Apps
The future of taxi app technology will witness a surge in the adoption of white label taxi app. These pre-built, customizable solutions offer a cost-effective and efficient way for businesses to launch their own branded taxi services. By leveraging white label taxi apps, companies can bypass the complexities of custom taxi app development while benefiting from a robust, feature-rich platform tailored to their specific needs.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to revolutionize taxi app technology. These cutting-edge technologies will enable advanced route optimization, predictive demand analysis, and personalized recommendations for users. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants will enhance customer support, providing seamless and real-time assistance to riders and drivers alike.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Connected Vehicles
The integration of IoT technology with taxi apps will pave the way for connected vehicles, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced safety features. Sensors and devices embedded in vehicles will transmit valuable data to the app, allowing for efficient fleet management, route optimization, and improved driver and passenger experiences.
Electrification and Sustainable Mobility
As the world moves towards more sustainable transportation solutions, taxi app technology will play a pivotal role in promoting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and facilitating the transition to eco-friendly mobility options. Apps will integrate features such as EV charging station locators, battery range management, and incentives for eco-conscious travel choices.
Multimodal Transportation Integration
Future taxi apps will seamlessly integrate various modes of transportation, including public transit, bike-sharing, and car-sharing services. This multimodal approach will enable users to plan and book end-to-end journeys, optimizing their travel experience and reducing reliance on personal vehicles.
Enhanced User Experience
With a focus on delivering exceptional user experiences, taxi app technology will prioritize intuitive interfaces, personalized recommendations, and seamless payment options. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) may also be incorporated to enhance the booking process and provide immersive visual experiences for users.
The Cost Factor: Taxi Booking App Cost
As the demand for cutting-edge taxi app technology grows, businesses must consider the cost implications of developing and implementing these solutions. While white label taxi apps offer a cost-effective option, custom taxi app development can be a significant investment, with costs varying based on factors such as features, integrations, and the complexity of the project.
To navigate the taxi booking app cost, businesses can opt for a phased approach, starting with a minimum viable product (MVP) and gradually expanding their app's capabilities as their user base and revenue streams grow. Additionally, partnering with experienced taxi app development companies can help optimize costs while ensuring high-quality, scalable, and future-proof solutions.
Conclusion
The future of taxi app technology promises to be an exhilarating journey, driven by innovation, customer-centric design, and a commitment to sustainability. As businesses strive to stay ahead of the curve, embracing emerging trends such as white label taxi app, AI integration, IoT connectivity, and multimodal transportation will be crucial for delivering exceptional user experiences and staying competitive in the rapidly evolving transportation landscape.
By leveraging the power of cutting-edge technologies and fostering collaborations between transportation providers, technology companies, and regulatory bodies, the taxi app industry can pave the way for a more efficient, convenient, and environmentally conscious future of mobility.
#hire developers#hire app developer#android app development#mobile app development#ios app development#taxi app development company
1 note
·
View note
Text
Revolutionizing Transit: The Rise of Smart Track Solutions
In the modern era, where urbanization is rapidly transforming our cities and the demand for efficient transportation is ever-growing, the need for innovative transit solutions has never been more critical. Enter "smart track solutions" – a paradigm shift in urban mobility that leverages cutting-edge technology to revolutionize the way we move within our cities. From intelligent routing algorithms to real-time passenger analytics, these systems are reshaping the urban landscape and enhancing the overall transit experience for millions worldwide.
At the heart of Smart Track Solutions lies the integration of advanced data analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) into traditional transit infrastructure. By harnessing the power of data generated from various sources such as GPS sensors, mobile apps, and smart cards, transit operators can gain valuable insights into passenger behavior, traffic patterns, and service demand. This data-driven approach enables them to optimize routes, schedules, and resource allocation in real-time, thereby minimizing congestion, reducing wait times, and improving overall operational efficiency.
One of the key components of smart track gps is predictive analytics, which allows transit agencies to anticipate demand spikes and proactively adjust service levels accordingly. By analyzing historical ridership data, weather forecasts, and special events calendars, these systems can predict future demand patterns with a high degree of accuracy. This enables operators to deploy additional vehicles or adjust frequencies on specific routes during peak hours, ensuring that passengers have a seamless and reliable transit experience.
Furthermore, Smart Track Solutions empower commuters with real-time information and personalized travel recommendations through mobile apps and digital signage. By providing up-to-date arrival times, service alerts, and alternative route suggestions, passengers can make informed decisions and navigate the transit network more efficiently. This not only reduces uncertainty and anxiety among travelers but also fosters a sense of trust and satisfaction with the transit provider.
Another innovative feature of GPS Vehicle Tracking System is dynamic pricing, which adjusts fares based on demand, time of day, and other factors. By implementing variable pricing strategies, transit agencies can incentivize off-peak travel, optimize revenue streams, and ensure financial sustainability in the long run. This flexible pricing model also promotes equity and accessibility by offering discounted fares to low-income riders or providing subsidies for essential services such as healthcare and education.
Moreover, Smart Track Solutions embrace sustainability by promoting multimodal integration and encouraging eco-friendly transportation options. By seamlessly integrating buses, trains, bicycles, and ride-sharing services into a cohesive transit network, these systems offer passengers a wide range of choices to suit their preferences and needs. This not only reduces reliance on private cars but also contributes to a greener and more livable urban environment.
In conclusion, smart track gps tracking system represent a game-changer in the realm of urban mobility, offering a holistic approach to transit planning and management. By leveraging data-driven insights, predictive analytics, and advanced technology, these systems empower transit agencies to deliver more efficient, reliable, and sustainable services to passengers. As cities continue to evolve and grow, embracing innovation in transit is not just an option but a necessity to meet the demands of the future.
Source Url:- https://sites.google.com/view/spatialtechnologysolutionscom4/home
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mobile Applications- The Secret Ingredient for the Success of the Transportation and Logistics Industry
If you’re here, the chances are that you are from the transportation and logistics industry. So, you can very well relate that in this increasing real-time economy, timing and speed are essential. Now, it may sound true for all the industries, but its significance on supply chains, transportation, and logistics could easily be doubled. That’s where mobile technology comes into the picture.
The automation phase is not something the logistics industry has seen recently. It has seen its share of phases with companies replacing manual labor with technology.
Mobile technology is not new to the transportation world. The early usage of mobile applications was mainly for navigation and location-based services. As of 2016, it’s used for applications focusing on engineering, education, traffic data collection, travel information ridesharing, and route planning.
The introduction of Qualcomm’s OmniTracs™ in 1988 and UPS’ roll-out of the DIAD (Delivery Information Acquisition Device) four years later are supreme examples of pioneering companies invested in mobile technology to drive efficiencies and create competitive advantage.
What led to the evolution of mobility?
Who doesn’t like remembering good old days, eh? Only the days were not so sorted back then!
Considering the complexity of the process itself, the industry still suffers from the issues arising from lack of automation and management inefficiencies; imagine what would have been the condition earlier.
Let us help you paint the picture:
● Loopholes in the logistic system: The lack of an efficient transport software created considerable loopholes in the logistics system, creating stagnancy and impacting truckload and less-than truckloads methods adversely within the supply chain. Speed, which is the soul of the industry, was becoming an obstacle in the absence of the automation software. ● Inconsistent Communication: The lack of communication across the organization increases the time-lag within the systems. Due to the lack of transparency and interdepartmental communication, the system’s optimization was next to impossible, resulting in a loss of clients and, ultimately, business. ● Management of Inbound Transportation: The hassle of managing inbound transportation in the absence of a properly integrated process leads to an increase in cost, damaging the delivery performance, and hampering the PO visibility. ● Tracking the delivery: Without software, tracking of supply and delivery was impossible. Leading to goods getting lost along with the delay in the process. Giving the client and the company’s nightmare!
Where are we today?
Smart devices have changed the entire spectrum’s faces, whether it’s enterprise companies, service providers, organizations, or even customers, so how could the transportation and logistics industry be left untouched!
It is now witnessing the latest innovations and breakthroughs in mobile technology. Here are a few stats to prove the point:
● Transportation and logistics companies can save almost 6.9 million dollars every year by implementing mobile devices throughout their companies. ● Organizations can save up to 4.2 million dollars if they deploy mobile, location-based technology. ● 60% of managers believe that broadband mobile communications will be their largest driver of ROI. ● 44% of managers believe that integrated vehicle telematics will be the largest driver of ROI. ● 38% of managers believed that radio frequency identification would improve ROI.
Let’s look at a few reasons responsible for such impressive stats, which further elaborate on why your business needs mobile technology:
The sophistication of processes
The primary business source for transportation and logistics companies is to deliver consignments from the manufacturing point to storage or delivery points. The success of which requires a smooth operation, punctuality in delivery, and speedy performance.
Using mobile technology, companies can not only achieve their consignment objectives but also give a competitive advantage to their customers.
Superlative tracking of cargo and productivity
Mobile technology provides unique real-time tracking features, which enable the customers to track their shipment and logistics companies to track their field employees’ movement accurately and effectively.
Improves Safety
Another significant advantage of mobile technology is that it enables effective communication between transit directors and drivers, ensuring a smooth and safe transition.
We can take Spain’s railway system as an example that uses a GSM network for high-speed train lines to ensure operational safety. The radio network equipment enables the conductors to communicate with the operation centers and with one another, allowing the trains to run smoothly without compromising on safety.
Improves Fleet Management
Mobile technology not just helps enhance safety in public transportation but also fleet management in the logistics business, as applications for route planning ensure that pickup and delivery are done more efficiently.
Nowadays, several route planning applications help businesses plan their routes, sharing updates such as traffic, any accidents or construction on the road, or even avoiding U-Turns downtown!
However, it’s not just the bed of roses situation. Mobile technology comes with its own set of challenges and weaknesses. Avoiding talking about them would be like ignoring the elephant in the room.
So let’s quickly have a look at the pointers which businesses need to either embrace or overcome:
● High development cost ● Internet could be a problem in certain areas ● Customer disloyalty towards your mobile application ● Confidentiality of information ● Competition
Now, before your mind starts getting cloudy with the dilemma that whether mobile technology is suitable for your business or not, let us give you a few examples of applications that have overcome the challenges and changed the transportation and logistics industry’s fate:
DHL Supply Chain
DHL is the global leader in supply chain management & third-party logistics, implementing innovative logistics solutions across various industries. Their DGF Cargo Mobile Tracking app offers tracking on the go with features like user shipping history, shipment status, and tracking details. The mobile app is available for free on iOS and Android, making DHL a consumer-first logistics business.
XPO Logistics Inc.
XPO Logistics is an American multinational transportation and contract logistics company that manages supply chains for 50,000 customers, including 69 of the Fortune 100. The Drive XPO mobile app is part of the XPO Connect digital freight platform that offers features like finding loads, negotiating rates, book freight, and many more.
UPS Supply Chain Solutions
UPS Supply Chain Solutions offers a comprehensive portfolio of services to enhance customers’ business performance, including logistics and distribution, transportation and freight, consulting, customs brokerage, and international trade services. Their offering: The UPS logistics app can help manage multi-location shipping from various locations, such as distributions centers, warehouses, and retail stores, with seamless integration and efficiency.
We talked about the past and where we stand today. But we understand that to come to any decision; a businessman needs to foresee the future. Keeping that in mind, let’s have a look at the future technology and trends that will rule the transportation and logistics industry in the coming years.
Mobile Computing
In today’s era, the consumer is dictating mobile consumption and driving the transportation market. Hence, the IoT is ensuring smart decisions in fleet management. It not only ensures the timely delivery but effective transportation of temperature-sensitive goods as well.
AI-augmented mobility
When powered by artificial intelligence, the transportation community can access the potential of data, cloud, and, most importantly, analytics to help reduce the time consumed in commuting, support air traffic, enable on the feet decision making, and really what not!
Frictionless travel
With a rise in mobility-as-a-service, innovations in micro-mobility, multimodal transportation enabled by mobility hubs, and platforms for ticketless travel, transportation planners can expect more seamless travel with minimal checkpoints and hindrance.
Digital identity
Digital technology is enabling improved security and driving a better experience for users, and thus, no wonder, transit and transportation industries are accepting the trend with open arms. The benefits like digital driver’s licenses for enhanced security, biometric, and facial recognition to improve efficiency and throughput at airports proves further that it is here to stay.
Cloud and Platform engineering
The evolution of cloud and platform engineering is bringing a change in attitude in the organization towards its core technologies, and transform their applications as per the changing expectations and needs of the customer. Breaking down the core technologies into microelements improves the visibility of risks associated with them, reduces them, and enhances user experience. This, along with the introduction of the DevOps mindset, improves the ability and speed of introducing new technologies. Thus, it proves to be the most significant facilitator of the transformation of core business applications over the next decade.
In the coming years, Transportation, Logistics & Supply Chain businesses will witness a shift towards Machine-to-Machine Communications to increase efficiency, security, tracking, monitoring, information, connectivity & collaboration. You could read more about emerging technologies in the logistics industry here.
Feeling all set to gather your team, sit down, and brainstorm the mobile application ideas tingling in your head while reading it? Great!
However, before you start working on the applications’ nitty-gritty, do you have enough resources to develop the app in-house? Or Do you want to create an app by saving time and money? If so, it is advisable to outsource to an app development company.
If you have never done outsourcing before, we understand you must be feeling like you need to take a step back and think about it! And yes! We also suggest you do that. Let us help you get started with some advice on things to look for in your application development companies…
Development Portfolio:
The logical first step is to ask the development company about the last few projects that they have delivered. This will give you a good idea of their past projects’ type and scale, and their competence vis a vis various technologies.
Operating System:
At the outset, it should be determined which platform is the best fit for your application. In case you haven’t decided, it is best to take inputs from your app developer. You may want to know whether the development company can build apps for different operating systems. Building cross-platform or hybrid apps also requires specific skills and experience, so it is wise to know whether the developer can handle those. There are deep guidelines for Android & iOS; therefore, the development company should have a thorough knowledge and experience.
UI/UX Design:
Developing an app is not just about coding; rather it is also about developing an attractive user interface. Creating a functional, easy-to-use design will not only enhance the appeal of your app but will also help you in achieving higher success during the marketing and promotions phase.
For these reasons, it is vital to ask the developers on their approach to user experience and design principles. That will help you in getting a clear vision of how the app is going to be designed. You might want to set out the expectations at this stage and point them in the right direction so that the prospective companies have a good idea of what you are looking for.
Pricing & Cash Flow:
When it comes to developing mobile apps, the oft-quoted advice is, “don’t let the price drive you.” In other words, your focus should be on developing a great product rather than a cheap product. It is good to have a flexible budget in mind and then choose the prospective company basis for their budgetary limitations.
Ease of Communication and Feedback:
Effective communication between clients and developers is essential for the success of any software development project. When you interact with a company, keep track of how often they communicate. Do they reply to your messages and phone calls actively? Are they keen to put forward their ideas and observations? You can try to judge whether they have a genuine interest in your project. If they are not eager to communicate at this stage, then it might be a good indication of how they will perform during development.
A decent app development company will actively participate in these discussions and be proactive in offering valuable inputs to help your needs. Based on their experience and knowledge about similar apps, they should be able to provide some useful insights and creative ideas for developing your application. This will help you determine if they are reliable enough to respond to challenging situations and keep your application development work on the right trajectory. Please feel free to ping us anytime, and let’s meet for a coffee cup to discuss how we can turn your dream into reality.Connect with us here.
Source https://bit.ly/31tKAKT
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Web & Mobile App Development
Tailored development of user-friendly and responsive web and mobile applications to enhance your online presence and user experience.
Cloud and AI-Driven Apps
Implementation of cloud-based and AI-driven solutions to streamline operations, enhance scalability, and leverage predictive analytics for smarter business decisions.
SAAS Solutions
Customized Software as a Service solutions designed to address your unique business needs, providing flexibility, scalability, and efficiency.
PAAS Solutions
Platform as a Service solutions offering a robust framework for application development, deployment, and management, empowering businesses with agility and innovation.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Enhance your website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs) through strategic optimization techniques, keyword research, content optimization, and technical enhancements, driving organic traffic and improving online presence.
Social Media Optimization (SMO)
Optimize your social media profiles and content to increase visibility, engagement, and brand awareness across various social platforms, leveraging audience insights, targeted messaging, and strategic campaigns for maximum impact and audience reach.
#ui ux design services#ai-based mobile apps#multimodal innovation#Digital Solutions#Web & Mobile App Development#Cloud and AI-Driven Apps#Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
1 note
·
View note
Text
What factors influence a Venture Capital (VC) investment decision for a certain logistics company?
Investment in logistics companies is majorly decided by three factors – Mutual Interest, Technology breakthroughs, and Innovations. The investment depends on the communal interest i.e., how the logistic company benefits the investor and in what ways. The pandemic accelerated the growth of the e-commerce industry, which has proportionally ignited the interest of VC investors in logistics operations. Investors for logistics are interested in funding companies based on e-commerce delivery apps, supply chain visibility, and last-mile logistics management. Companies that have innovative strategic solutions are more likely to attract funding.
The second aspect depends on technology breakthroughs, such as cargo and shipment monitoring technologies (GPS trackers, Bluetooth, RFID sensors, IoT (Internet of Things), AI/ML, Big Data, and Cloud). Technology is changing every aspect of how logistics companies operate. The winners will be those who understand how to use technology and those who don't risk becoming obsolete. Companies with a clear digital strategy integrated into their business strategy will be preferred over others.
Finally, it has been seen that investors prefer companies that are open to the adoption of new ideas and digitalization. For instance, on-demand delivery for groceries has emerged as an investor favorite, with massive inflows of venture capital funding into this category. Adhering to customer expectations and continuously working towards improving efficiencies are also factors that seal the decision for investors. Best logistics companies that focus on increasing the engagement of customers using mobile apps and websites to track orders and shipments are in high demand by investors.
Area of Transportation is Receiving the Most Attention
Startups offering last-mile delivery services to retailers and individuals are attracting maximum investment, especially startups that rely on unconventional delivery modes, such as crowdsourced delivery, drones, autonomous vehicles, and shipments to parcel lockers. Investors clearly see an opportunity in innovative last-mile service providers.
Electric vehicles, drones, and digitization have all been making inroads in the transportation sector over the last five years and it is changing the movement of goods. Investors see an opportunity in all three areas of transportation. Considering driver shortage and congestion issues, technology-enabled, autonomous vehicles are becoming increasingly important and viable. There is the pressure of decarbonization, and top transportation and logistics companies are expected to drive the change with the use of electric vehicles (EVs), multimodal connectivity, and others that would help in creating a carbon-friendly environment. In the future, we will also see the use of robots and drones inside warehouses and other open spaces. Drones can also help in achieving short-mile deliveries. For instance, a track can pull up in a residential area, with several AI-enabled drones that can go out and deliver to the desired location. This can improve the different sectors of the economy and scale up growth.
#logistics#logistics company#logistics services#logistics solutions#Logistics service provider#transport
1 note
·
View note
Text
Seoul National University plan to use Zero WiredTM to develop AI-based seizure detection medical device

Seoul National University plan to use Zero WiredTM to develop AI-based seizure detection medical device. Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Presents Study of SK Biopharmaceuticals' Seizure Detection Wearable Device at AES 2022. Poster session features a preliminary study result of potential seizure monitoring and detection for patients using SK Biopharmaceuticals' wearable device SK Biopharmaceuticals, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital plan to use Zero WiredTM to further pursue clinical research and develop it into an AI-based seizure detection medical device PANGYO, South Korea, Dec. 4, 2022 - Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (SNUBH) presented its preliminary study result of seizure monitoring for patients with epilepsy using SK Biopharmaceuticals' multimodal wearable device at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) Annual Meeting 2022 in Nashville, Tennessee, December 2-6. This is the first study of the wearable device developed by SK Biopharmaceuticals, an innovative global pharmaceutical company. A SNUBH research team led by Prof. Hunmin Kim conducted the study from March 11, 2021, to March 10, 2022, with 14 patients aged 9-27 regularly using the device for more than a month. The wearable device monitored patients daily and recorded seizure data on a mobile app while measuring bio-signals such as brain electrical activity (electroencephalography, EEG), heart rhythm, and body movement.

Prof. Kim said at the AES that it has shown to be useful in collecting data for potential seizure detection as it continuously measured brain activity for more than 8 hours and transmitted the data to a server in real-time. During the 3,723 hours of recording, it identified 1,686 seizures. SK Biopharmaceuticals and SNUBH plan to further pursue clinical research with Zero WiredTM, aiming to develop it into an AI-based seizure detection and forecast device. Zero Wired, a CES® 2023 Innovation Awards Honoree, is an upgraded version of the multimodal wearable device used in the SNUBH pilot study. SK Biopharmaceuticals and its U.S. subsidiary SK life science are global pharmaceutical companies focused on the research, development and commercialization of treatments for disorders of the central nervous system (CNS). The companies have a pipeline of eight compounds in development for the treatment of CNS disorders, including epilepsy. Additionally, SK Biopharmaceuticals is focused on early research in oncology. Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders. There are approximately 50 million people living with epilepsy worldwide, and 3.4 million people in the U.S as per World Health Organization. Epilepsy is characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures. The seizures in epilepsy may be related to a brain injury or a family tendency. Epilepsy has many different causes. About half of people with epilepsy have an unknown cause as per Epilepsy Foundation. Having seizures and epilepsy can affect one's safety, relationships, work, ability to drive, and much more. People with epilepsy are at risk for accidents and other health complications, including falling, drowning, depression and sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (SUDEP). Despite the availability of many antiepileptic therapies, more than one-third of people with epilepsy are not able to achieve seizure freedom, meaning they have epilepsy that remains uncontrolled. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Future of work
Forecasting emerging technologies impact on work in the next era of human-machine internships
ABOUT INSTITUTE FOR THE FUTURE
Institute for the Future (IFTF) is the world’s leading futures thinking organization. For over 50 years, businesses, governments, and social impact organizations have depended upon IFTF’s global forecasts, custom research, and foresight training to navigate complex change and develop world-ready strategies. IFTF methodologies and toolsets yield uncommonly coherent views of transformative possibilities across all sectors that together support a more sustainable future. Institute for the Future is a registered 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization based in Palo Alto, California.
DELL TECHNOLOGIES
Dell Technologies is a unique family of businesses that provides the essential infrastructure for organizations to build their digital future, transform IT and workforce and protect their most important asset, information. The company services customers of all sizes across 180 countries—ranging from 99 percent of the Fortune 500 to individual consumers—with the industry’s most comprehensive and innovative portfolio from the edge to the core to the cloud.
ABOUT THIS RESEARCH
Dell Technologies partnered with the independent futures research group Institute for the Future (IFTF) to explore how emerging technologies could reshape the work environment over the next decade. The research builds on the organizations’ collaboration in 2017, when IFTF distilled informed opinions from 20 experts from around the world to forecast the “next era of human-machine partnerships.” Two years later, IFTF is forecasting how a new dynamic between humans and machines may inform the future of work. To execute this inquiry, IFTF relied on its decades-long study on the future of work and technology, and an expert workshop held in Palo Alto, California in November 2018 with participants from across the globe.
INTRODUCTION
The technologies that are emerging today already make it possible to more aptly match the right work to the right person regardless of their gender, age or geographic location. Imagine if, as the day-in-the-life scenario below depicts, job seekers in 2030 routinely demonstrated competencies to potential employers through mobile gaming apps.
Emerging tech today is not only creating new possibilities for how people and jobs find each other more seamlessly, they are also enabling new ways of working together. These advancements in technologies will require new skills and capabilities for workers to excel in the 2030 work environment.
This report explores how collaborative AI, multimodal interfaces, extended reality (XR), and secure distributed ledgers will intersect with evolving social and economic forces to shape how we prepare for, find and work in 2030. It builds on a 2017 Institute for the Future (IFTF) report entitled The Next Era of Human-Machine Partnerships, which forecasted that partnering with machines will help make the most of the complementary strengths of humans and machines. Since then, IFTF and its consortium of global experts have been exploring how these partnerships will transform our lives, the way we work and the economy by 2030 in a three-part research series. The insights provided by our experts inspire new possibilities and help inform IFTF’s forecast of three shifts that have the potential to recast the future of work, and open the door for more people and communities to pursue meaningful, creative and sustaining work.
Technological advancement is one undeniable force that will impact the future of work, but how these and other emerging technologies shape the future for workers is up to us. Without deliberate effort to apply emerging technologies to promote a more inclusive and equitable work environment in 2030, the advances in technology may not yield as positive a future.
We invite you to read on to uncover examples of emerging technologies stimulating and enhancing collaboration today, as well as the tectonic shifts that human and machine partnerships could spur to help reshape the future of work. As exciting as the possibilities may be, this future is not guaranteed; our experts also identify key dilemmas that will need to be overcome to cultivate a more equitable and inclusive future to empower the next generation of workers.
A DAY IN THE LIFE—2030 LAGOS, NIGERIA
Ndidi messages her friends that she got the gig. The process was typical: after attending a friend’s recruitment event for his social VR company, she got an invite code to play a recruitment game and she followed through, squeezing in time to play it on her device during her commute. The game was fun and she felt immediate gratification when she leveled up quickly. Ndidi scored high in intellectual curiosity and attention to detail, and her results indicated that she was skilled in spatial reasoning, a strength she didn’t know she possessed. She had strong leadership potential, it said. A gig offer from an immersive architecture firm came not 48 hours later.
The changes to work and learning in 2030 will be enabled by the maturation and proliferation of today’s emerging technologies. These technologies will birth new industries, jobs, places of work and working patterns. Four emerging technologies are critically important to understand how humans and machines might work in concert with each other to better match people to meaningful, creative and sustaining work, and improve collaboration within and between organizations. These technologies are collaborative AI, multimodal interfaces, extended reality (XR), and secure distributed ledgers.
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES THAT REARCHITECT THE WORLD OF WORK
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
The Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence aims to build common sense into machine systems so that they can be better collaborative partners for humans.ii Recently, its computer vision research team Perceptual Reasoning and Interactive Research (PRIOR) released a collaborative game in which the AI system uses its ability to reason and make inferences to communicate with a human partner. In the game, the AI and its human partner trade off illustrating scenes to try to understand what the other has drawn. Rather than looking to outperform a human (such as in a chess match), the researchers at PRIOR are building machine systems that can better communicate and interact with human partners.
Collaborative AI
“The robots are coming for our jobs” has been a common concern expressed in discussions about AI. What underpins this sense of anxiety over job competition and scarcity is the concern that advancing AI systems will be sophisticated enough to do the work that humans do today. A more useful reframing articulates the relationship between human and machines as a partnership, through which the two groups work together to achieve more. Working within this framework, it is possible to envision cooperative AI systems in which human strengths are programmed and integrated into machine intelligence. Just as humans need to improve our ability to offload tasks that are better suited for machines, so will AI systems need to be designed to recognize computational limitations and know when to lean on their human partners for help with completing a task.i AI explicitly designed for collaboration will help build capacity in machines to improve their understanding of humans.
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
Ultrahaptics creates tactile sensations that do not require controllers or wearables.iii Users can control buttons and sliders with ‘mid-air haptics’ without having to touch the surface of the technology.
Interacting without physically touching the technology can keep public technologies such as kiosks and ATMs cleaner. Gesture interfaces can also improve safety in medical environments and in vehicles because it helps keeps users’ focus on where it should be and away from the device.
Multimodal Interfaces
The modalities of seeing, hearing and touching have been the more commonly used human senses in human-machine interactions. Emerging interfaces are integrating haptic feedback, gesture recognition and even smell to provide alternative mediums for displaying and interacting with data. Multisensory integration will expand the possibilities for form factors, diversify the user experience and make machines more accessible to different types of users. Imagine when workers can access data using gesture recognition, or when smell becomes integrated into VR experiences.
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
Etch is a smart contract-based payroll platform that allows for real-time payment of wages.iv Built on top of the Ethereum blockchain, Etch seeks to the reduce the administrative burdens associated with payroll and accelerate the pace at which people can get paid. Promoting their service as “the first evolution in payroll since the Industrial Revolution,” Etch offers an alternative way for employees to be paid. Instead of being a dependent on employers’ payroll structures, a smart contract pay system like Etch makes it possible for workers to receive their wages in real time.
Secure Distributed Ledgers
Secure distributed ledgers like blockchains provide an immutable, transparent data storage mechanism, allowing all parties to access all transaction data. They enable applications like smart contracts, where transactions are algorithmically triggered when objective criteria are met. By 2030, smart contracts will be connected more seamlessly to real-world events. This will facilitate the ability to automate a whole host of activities, including real-time compensation that is linked to the completion of a work task.
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
Interplay Learning uses Virtual Reality (VR) and 3D simulation-based training software to train HVAC and solar technicians, making it easier for workers to gain new knowledge and skills.
Workers have access to over 100 hours of scenario-based learning coursework via their phone, computer or in VR to advance their learning on their own time. vi
Extended Reality (XR)
Current technologies blend digital and physical worlds; the two will become even more intricately overlaid over the next decade, enabled by more innovative experimentation with extended reality (XR). XR, which includes augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR), combines real and virtual environments and encompasses all human-machine interactions generated by computer technology and wearables.v The blended environments allow users to turn what is otherwise abstract information into rich, interactive experiences. By 2030, more organizations will rely on XR to superimpose a virtual layer over physical spaces to experience and share content on any computing device.
OPPORTUNITIES FOR HUMAN-MACHINE PARTNERSHIPS
Increasing opportunities for more people and communities to pursue meaningful, creative and sustaining work is the cornerstone of both national and global efforts to improve economic prosperity by 2030, particularly for women and young people. In fact, the United Nation’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which came into effect on January 1, 2016, states, “We will work to build dynamic, sustainable, innovative and people-centered economies, promoting youth employment and women’s economic empowerment, in particular, and decent work for all.”vii
The human-machine partnerships emerging over the next decade can help realize the goals and targets outlined by the United Nations and echoed in national policies across the globe. They offer the possibilities to create more equitable ways to prepare and connect people, particularly youth and women, to income-generating opportunities. And human-machine partnerships enable novel approaches to spreading decision-making and collaboration across networks of workers.
This section describes the three shifts that could help shape a more inclusive and rewarding work environment over the next decade. The forecasted shifts are:
Inclusive Talent; Empowered Workers; AI Fluency
SHIFT 1 : INCLUSIVE TALENT
A DAY IN THE LIFE—2030 LONDON, ENGLAND
For hiring manager Lydia Kim, a new employee’s first day is often the first time she sees the person she has hired. She knows they are competent; the AI system her company uses to spot and recruit talent has an admirable track record in finding people ready and prepared to contribute on day 1. She knows their personality; she has interviewed them in a social VR space and observed them working with others from the organization in virtual simulations. But how the potential hire has chosen to present herself in these virtual locations is up to her. So, what she often doesn’t know when she offers them a job is their age, gender and, unless required for the job, their geographic location. With the benefit of an AI system that can evaluate an individual’s ability based on their competencies and assess their potential as well, Lydia and her team have overhauled their hiring process. Their new way of finding people has expanded their pool of potential talent and helped the organization meet their stated goals around diversity and inclusion.
Recent advances in deep learning are making it possible for powerful algorithms to identify skills and capabilities that are not explicitly described on a résumé. New software systems can help create a richer picture of an applicant by extrapolating relevant skills related to their hobbies and past experiences, and through applying contextual information about how other workers from the same educational institution or learning pathway have fared in the position. The ability to include a diverse set of inputs into the hiring process may reveal new insights to employers—about the expertise, traits and potential of the ideal candidate, for example, which could extend the talent pipeline to include people with a wide range of backgrounds and experiences.
In Lagos, Nigeria, West African Vocational Education (WAVE) aims to create a new set of norms and practices around hiring. To include more people with diverse backgrounds and experiences, WAVE finds, screens, trains, places and supports West Africans between the ages of 16 and 30 in hospitality and retail jobs. They do this through what the social venture calls “a double-sided financial model” in which both the trainee and the employer shoulder some of the cost. According to WAVE’s CEO Misan Rewane, assessment tools should be designed to allow potential hires the opportunity to “show rather than tell” future employers their ability to succeed on the job. Rewane argues that most employers don’t know which competencies are accurate predictors of job performance. Proxies, like degrees and work experience, she cautions, might predict “confidence and quick reasoning, but little else.”viii Applying emerging technologies to the work of identifying appropriate talent may enhance an organization’s strategic efforts around diversity and inclusion. Over the next decade, machine-learning systems will form partnerships with humans to support the challenging work of hiring and retaining talent. This will ease the way for people, notably women and younger workers, to be evaluated not only by their compatibility with the present-day workforce or their past performance (or lack thereof), but on their future contributions and how they align with the desired direction for an organization.
SHIFT 1: INCLUSIVE TALENT
Tools that improve an organization’s ability to identify new talent will help build out the workforce in growing 21st century industries like gaming and Esports, already multi-billion-dollar industries. The next million gamers (to add to the approximately 2.4 billion who already play) are expected to come from countries such as Kenya, Nigeria, China, India, Mexico and Brazil.ix This growth will drive the need to create culturally relevant content. To meet that demand, organizations will need to be able to better evaluate the skills and knowledge that the generation which has grown up playing what one expert called “hard-core games” will bring to the workforce.x
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
Eightfold combines Applicant Tracking System (ATS) and Human Resource Information System data with publicly available data to uncover the ideal candidate for a given position. It also employs ‘candidate masking,’ withholding all evidence of personal characteristics (age, gender, ethnicity, geography) from hiring managers before interview selections are made.
New offerings, such as Eightfold’s Enterprise Talent Intelligence Platform, may improve humans’ ability to evaluate seemingly unrelated skills and knowledge, along with personality traits and interests to determine if someone is a good fit for an open position.xi Other services, such as Knack, which combines video games, behavioral science and AI, will help uncover skills and capabilities unknown to both the individual and employers.xii And digital credentialing platforms, such as Credly, which aims to build a “common, verified language” for skills and demonstrated competencies, will facilitate organizations’ ability to understand applicants’ learning histories and better recognize individuals’ full potential.xiii
Notably, by 2030, inclusive talent practices may reveal as much to employers about their own assumptions around hiring as they will help people find the right positions.
Employers and hiring managers may gain a more precise understanding of the skills, aptitudes and personalities that help an individual succeed in their organization. These emerging human-machine partnerships will enable them to experiment with new types of workers to inform how they form teams and design incentives to increase productivity, morale and retention.
SIGNAL OF CHANGE: Knack aims to uncover the ‘hidden potential of every person’ by using digital games, behavioral science and AI to match individuals’ personal strengths with professional work. The start-up measures human potential and catalogs them as knacks (traits and abilities), superknacks (potential to do well in a career) and ultraknacks (customized for a specific employer).
SHIFT 2: EMPOWERED WORKERS
A Day in the Life – 2030 Beijing, China.
The burgeoning field of genomic medicine is built on collaboration. Most scientists and clinicians engaged in understanding and treating people with genetically defined diseases operate under no false pretense that their scientific discovery or successful treatment is the sole result of their individual effort, or even the work of a small team. Metabolic Geneticist Li Min, like almost all of her colleagues entering the field of genomic medicine in the late 2020s, was trained to be networked scientist, and to conduct distributed research in realtime. The collaborative platforms she uses (often multimodal and XR) first gained popularity in the gaming world but are now routinely integrated into her research practices. Incentives have evolved to reflect the norms and practices in genomic research. Publishing first—that is, being listed as the first author in peer-reviewed biomedical journals—is not as highly valued as before. Credit for any advancement in the scientific community’s understanding is automatically tracked and attributed to the people and AI systems involved in the work. The complexity and scope of the scientific challenges being tackled in 2030 require a coordinated approach by thousands if not millions of humans and machines. Dr. Min and her contemporaries are leading the way in re-organizing research labs and clinical practices to support this new way of networked working.
A growing movement to design work infrastructures that promote collaboration and reward contribution is taking shape. Gaming and coding communities hint at the ways that people will collaborate to get stuff done. Innovative organizations are experimenting with reputation-weighted decision making, automated profit-sharing payrolls, and open, mutable policies and codes of conduct. Over the next decade, a new organizational structure will emerge that decentralizes decision-making and empowers workers. It will be enabled by a number of technologies including secure distributed ledgers and machine-learning systems.
Data for Democracy is a 4,000-member organization with members residing in every time zone across the globe.xiv To work collectively to advance their issue of ensuring that data and technology are used for good, it relies on human-machine partnerships to empower its members.For instance, the organization’s projects operate in Slack channels, a single place for contributors to share messages, tools and files.xv It even onboards new members in a Slack channel. Slack, explains Data for Democracy founder Jonathon Morgan, is its own “ecosystem” for coordinating projects and hackathons.xvi
Working in self-selecting channels as opposed to on fixed teams has not detracted from a sense of community. In fact, says software developer Margeaux Spring, “Data for Democracy is the most welcoming, helpful and safe virtualspace I have ever participated in.”xvii The infrastructure that fosters trust also yields results. To date, the group has completed 20 projects with 29 in progress, logging over 267,000 Slack messages in the process.xviii
Sharing many of the functionalities of Slack, the messaging app Discord provides a robust but lightweight way for gamers to connect and strategize with other players inreal-time, using text, voice or video. Since 2015, Discord has amassed more than 130 million users who participate in user-generated servers, which operate like chatrooms, that have subtopics and search capabilities.xix Another collaborative platform, Github, was originally viewed as a tool for developers to host and review code and build software together. Now, Github is home to wide-ranging projects undertaken by distributed communities.
Collaboration platforms such as Slack, Discord and Github offer clues to the social norms, cultural practices and workers’ expectations that will inform how work is completed a decade from now. For teams that are geographically distributed, these tools help facilitate constant connection and coherent, team-based actions.
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
Discord is a free voice, video and text chat app, highly popular with players of strategy games in which team communication is critical. For a significant portion of the 14 million daily users (who, on average, collectively send over 315 million messages each day), it provides a community of like-minded people interested in accomplishing (game-related) tasks together.
Over the next decade, organizations that aim to foster collaboration will work to empower workers by cultivating the real-time collaboration practices already embedded in gaming, coding and distributed communities.
The forecasted shift toward empowered workers may lead to a greater number of decentralized organizations that operate more like Data for Democracy or a gaming community than they do a traditional organization. Start-up Colony’s goal is to build the governance framework for these types of organizations. Built on the Ethereum blockchain, the platform “automates the project management process by aggregating the collective intelligence of the workforce to suggest and assign tasks, make decisions and provide feedback on people’s work.”xx Colony envisions a future of self-organizing companies that “run via software not paperwork,” and in which, according to CEO Jack du Rose, “the relationship is with the contract, not with the company.”xxi
Companies running on software may make monitoring and quantifying workers’ contributions much easier, which may lead to new practices around compensation. Imagine if workers could choose how frequently they want to be paid. Some may prefer to be paid monthly or bi-weekly, however, others may choose to be paid as soon as they earn it— daily, hourly or even in real time. According to Euros Evans, CEO of a London-based start-up called Etch, “We hope by people being paid as soon as they’ve earned it, we can reduce the need for payday loans and other such instruments to plug spending gaps, as well as improve peace of mind.”xxii Over the decade, real-time payroll could extend to real-time profit sharing, triggered the moment the profit is realized by an organization.
Similarly, some workers will be motivated by more than a paycheck. For some, it might be self-actualization, or the ability to employ their knowledge in a meaningful way. To keep pace with the diversity in motivations, organizations will need to pursue a portfolio of compensation resources that spans beyond monetary.
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
Colony constructs the tools people need to be able to quickly and easily work together to accomplish a discrete task. As CEO Jack du Rose explains, instead of relying on Upwork, groups can tap a “network of people that you already trust… but do not need to be on payroll all of the time.”xxiii As a next step toward a more open workforce, Colony’s upcoming application will give teams a hub for incentivizing and organizing open contributions to their projects.
SHIFT 3: AI FLUENCY
A DAY IN THE LIFE—2030 BUENOS AIRES, ARGENTINA
After two years working as a systems programmer for a large hospitality chain, Laura invests more of her personal time in virtual learning courses on positive psychology and behavior change. Before taking a full-time role, Laura had concentrated most of her course work on intelligent agent design, learning the ins and outs of robotics AI programming. Now, with a couple of years of work experience, Laura has figured out that her technical expertise is less valuable than her ability to work with the company’s AI systems. She is part of the cohort of AI natives who have joined the workforce over the last few years. Unlike digital natives, millennials and other more experienced workers at her organization, she grew up navigating her coursework and personal life with her infallible AI assistant at her side. Working in partnership with an AI assistant is second nature to her, but Laura has noticed that many of her colleagues who didn’t grow up with AI struggle to integrate it into their workflows. So, instead of re-programming the company’s AI systems, most of her time at work is now spent helping her colleagues partner more smoothly with those systems. Laura doesn’t know if some of her Gen X colleagues will ever stop writing their own emails, but, the mentoring by AI natives like herself is a step in the right direction.
The future of work is inextricably linked to the future of learning. How we educate our youth translates into their preparedness as they enter the workforce. And how we retrain and upskill our existing workforce allows them to stay relevant in a changing work environment. The learning, retraining and upskilling over the next decade will include improving everyone’s knowledge of and capabilities in AI. And this won’t necessarily mean teaching coding or even broader technical skills. In a new world of work, learning to effectively judge what machines can and cannot do, as well as what they should and should not do, will be a critical capability for workers in the future. In return, human strengths and capabilities will need to be integrated into AI systems to help workers partner more collaboratively with them. Classifying the strengths and capabilities of both humans and machines will be a core aspect of having a strong command of AI systems in the future.
There is little debate that the pace of change is accelerating—and with it, the rate at which people acquire the ever-evolving skills and knowledge they need to execute their jobs. Yet, our ability to prepare today’s learners for tomorrow’s work is hampered by a lack of shared understanding of what people will need to know to be successful in the 2030 work environment.
At minimum, experts forecast that workers’ skills will include a set of capabilities needed to apply AI effectively in their work. A 2017 study published by MIT Sloan Management Review identified three categories of AI-driven business and technology jobs: “trainers, explainers and sustainers.”xxiv According to study authors James Wilson, Paul Daugherty and Nicola Morini-Bianzino, AI trainers will be needed to develop AI personalities and train them to convey empathy; AI explainers will be enlisted to elucidate algorithmic decision-making; and AI sustainers will seek to prevent AI from doing harm.
Increasingly, consensus is forming among experts that it is the partnership between humans and machines that will have the most potent impact. As Wilson and Daugherty argue, the greatest benefit of AI “will be in complementing and augmenting human capabilities, not replacing them.”xxv Others, like Dennis Mortensen, CEO and founder of x.ai, echo that sentiment, viewing the introduction of AI as something that will make us “better at doing our jobs, and better at being human.”xxvi And, Mihir Shukla, chief executive of Automation Anywhere, envisions of a future of work in which bots are seen as “digital colleagues.”xxvii
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
x.ai built Amy and Andrew, autonomous AI scheduling assistants, to help, as the company’s CEO explains, “automate everything you can” to free up human’s time and attention for higher-order thinking.xxviii
To create future work environments in which machines are viewed as colleagues and the comparative advantage of humans lies in our higher-order thinking and emotional intelligence, human strengths will need to be programmed and integrated into the machine intelligence. Just as humans need to improve our ability to offload tasks that are better suited for machines, AI systems need to be designed to recognize computational limitations and know when to lean on their human partners for help with completing a task.
Though these may include application or industry-specific skills—it may be a kind of meta-knowledge about AI, or a deep understanding of human and machine systems, that sets workers apart. Over the next decade a type of AI fluency may emerge. For humans, AI fluency will include knowing how to leverage machine intelligence to manage workflows and accomplish tasks as well as knowing the limitations of the AI systems. And, the ability to know when a human is better suited to complete a task or set of activities will be a form of human fluency that machines will need to develop. Importantly, keeping pace with how each other’s evolving capabilities might be changing will be part of building fluency in AI.
Interestingly, many skills that experts view as part of AI fluency are not, today, universally recognized as skills at all. Compassion and judgment, for instance, are often thought of as innate traits. But the emergence and success of programs like Stanford University’s “Compassion Cultivation Training” suggest that people can learn them as skills. In addition, a present-day education in tech can leave out discussions of how to create systems where there is responsibility, transparency and accountability. However, examining what these values mean and how to implement them will be critical for developing true AI fluency.
By 2030, AI fluency will not necessarily mean knowing coding languages. A machine can catalogue facts and figures faster and more comprehensively than any human, but, many experts agree, understanding the context those facts fit within is something humans will likely remain uniquely capable of between now and 2030. Ultimately, the experts’ perspectives suggest, to some degree, we may have to rethink and rescope what we consider skills in the first place.
SIGNAL OF CHANGE
Stanford University offers an 8-week course taught by clinical psychologists, researchers and scholars to help people train their minds “to intentionally choose compassionate thoughts and actions and develop skills that help you relate to others.”xxix Executives and managers are encouraged to attend. Stanford faculty in Psychology, Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and Neuroscience are actively engaged in understanding compassion and altruism to help reduce distress for individuals and improve relationships.
NAVIGATING DILEMMAS: PREPARING FOR HUMAN- MACHINE PARTNERSHIPS’ IMPACT ON WORK
One of the primary objectives of undertaking a study of what work might look like in 2030 is to spark actions today, actions that help accelerate and spread the conditions anticipated in the future, or actions that prevent or slow them down. If our collective interest is to increase opportunities for more people and communities to find meaningful, creative and sustaining work, then anticipating hurdles and leveraging the affordances that the emerging human-machine partnerships offer are critical actions to take in the present. As we further engage with new technologies, we will discover future dilemmas that we must successfully navigate to fully realize human-machine partnerships. These dilemmas include algorithmic bias in work environments, a digital skills gap and a re-examination of workers’ rights and protections on the global scale.
Algorithmic Bias
Using human-machine partnerships to improve the process of connecting people to the right job is relatively new to how most organizations hire. While there are many favorable advancements and novel solutions that promote more inclusive hiring, there are a number of risks to consider. First and foremost, we must challenge the assumption that hiring managers know what constitutes an ideal employee. The fact may be that many organizations don’t actually know what type of person with which mix of skills excels in their environment. To generate large, robust models, we will need more data not only about potential hires but also data about how past hires have performed. The data, generally considered proprietary, will improve the machine-learning systems, and they will help expose biases and unseen hiring practices of organizations.
For human-machine partnerships to enable more inclusive talent practices, we also need to do more to understand algorithmic bias. People seeking work must be able to understand how their profiles are being interpreted by the machine-learning tools that employers will use to inform their hiring decisions. As professors Peter Cappelli, Prasanna Tambe, and Valery Yakubovich wrote in a 2018 white paper, “The outcomes of human resource decisions (such as who gets hired and fired) have such serious consequences for individuals and society that concerns about fairness—both procedural and distributive justice— are paramount.”xxx And organizations will need to be steadfast in ensuring that their systems’ decision-making algorithms align with their values. Ethical practices, including full visibility to the factors informing algorithmic hiring models, will be essential to prevent biases and for these tools to promote a shift toward inclusive talent.
Digital Skills Gap
As worker evaluation practices change and new methods of discovering talent emerge, it is possible that by 2030, older generations may feel shut out of parts of the economy.
Using gamification in systems to test applicants’ or employees’ aptitudes may reward younger people who have grown up gaming. And a lack of familiarity with collaborative platforms and working in networks may also hinder some workers’ ability to take full advantage of the 2030 human-machine partnerships. This is a concern that workers and managers have already expressed. According to 4,600 global business leaders, 54% forecast the next generation of workers will disrupt their workforce with their ingrained digital skills and mindset, and 58% agree that they’ll struggle to provide equal opportunities to multiple generations of workers.xxxi
As new workers conditioned to gaming and to the quick pace of change enter the workforce and rise in the workplace, seniority may count for less. Organizations will need to be prepared to upskill seasoned, experienced workers in new ways of working and learning. One way this may occur is through cross-generational or reverse mentoring, where younger colleagues advise on topics such as technology and change management. This reversal of the mentoring relationship is occurring now. According to research with 12,000 Gen Zers, 77% of young respondents are willing to mentor older co-workers in tech.xxxii
Workers’ Rights and Protections
The shift toward empowered workers challenges us to think about the role of national and local oversight over work arrangements. If one of the objectives of a distributed organization is to decentralize opportunity such that anyone qualified to accomplish a task can do so irrespective of where they live, what are the labor policy changes that would need to be put into place? If people are being compensated for their contributions and not for a fixed amount of time, how will workers’ rights and protections be upheld and enforced?
In certain countries, full-time employment is the means by which people receive financial protections for their individual and family’s healthcare, contributions to retirement pensions and guaranteed pay for sick or vacation time, among other benefits. Let’s say an emerging technology such as secure distributed ledgers grant people the ability to seamlessly create work agreements. How then will people navigate the different laws and regulations associated with workers? How will they do so in a way that is fair to workers? It may be that in order to realize a more equitable future for work, governing structures will need to keep pace with these changing work arrangements.
Conclusion
As we consider the future for the individual who acquires a job via machine-learning systems that measure human potential through gameplay, we have to think more deeply not only about new hiring practices, but also about what her work itself will entail. As she pursues a 21st century career path, she’ll begin to cultivate a trusted community of colleagues. Will she then build a collaborative organization with some of them in which governance is allocated according to their contributions? Or will she get hired by an established organization with nondiscriminatory practices (where age, gender, ethnicity and geography are not included in the vetting process)? Indeed, will the fact that she is an AI-fluent woman living in Lagos, Nigeria who lacks professional experience but is an avid gamer, be seen as an invaluable asset to her employer?
The next decade brings with it an opportunity to apply emerging technologies such as collaborative AI, multimodal interfaces, extended reality and secure distributed ledgers to shape the future such that more people can engage in meaningful, creative and sustaining work. This report argues that these technologies can enable three shifts—inclusive talent, empowered workers and AI fluency—toward a reimagined future for work, one in which the human-machine partnerships forming over the next decade produce a more inclusive and equitable future.
This opportunity is not a foregone conclusion, however. Technological advancement is one undeniable force that will shape the future of work. It is already happening: AI is entering the workplace today at a rapid clip, offloading certain tasks and displacing workers from jobs. Without deliberate effort to apply emerging technologies to promote a more inclusive and equitable work environment in 2030, the advances in technology may not yield as positive a future. With the benefit of a long view, however, we can imagine how AI in the workplace can generate a variety of new work roles and create “new, uniquely human” jobs.xxxiii
Emerging technologies are just part of the picture. They will intersect with other social and economic forces to create new tensions and challenges. Navigating the dilemmas outlined in the report will require a thoughtful, imaginative and forward-looking approach. By applying the insight gained by looking out ten years, we have the opportunity to strengthen the partnerships between humans and machines and bolster opportunities for economic empowerment and decent work for all.
Designit, “Collaborative AI Will Revolutionize the Way We Work and Interact” in Medium (Dec 1, 2017) https://medium.designit.com/ collaborative-ai-will-revolutionize-the-way-we-work-and-interact-65cebd11308c
Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence, https://allenai.org/about. html
Ultrahaptics, https://www.ultrahaptics.com
Etch, https://www.etch.work
North of 41, “What Really Is the Difference Between AR / MR / VR / XR?” in Medium (March 20, 2108) https://medium.com/@ northof41/what-really-is-the-difference-between-ar-mr-vr-xr-35bed1da1a4e
Interplay Learning, https://www.interplaylearning.com/
United Nations, “Transforming Our World: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development” (September 25–27, 2015) https:// sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld. The agenda states: “27. We will seek to build strong economic foundations for all our countries. Sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth is essential for prosperity. This
will only be possible if wealth is shared and income inequality is addressed. We will work to build dynamic, sustainable, innovative and people-centred economies, promoting youth employment and women’s economic empowerment, in particular, and decent work for all. We will eradicate forced labour and human trafficking and end child labour in all its forms. All countries stand to benefit from having a healthy and well-educated workforce with the knowledge and skills needed for productive and fulfilling work and full participation in society.”
Misane Rewane, email message to author, February 26, 2019.
“Afrofutures: Exploring Speculative Art and Design,” presented at IFTF’s 2018 Annual Ten-Year Forecast Festival at the Computer History Museum, Mountain View, CA, September 26, 2019
Sebastian Benitez, expert workshop held at Institute for the Future in Palo Alto, California in November 2018.
Eightfold AI, https://eightfold.ai/technology/ xii Knack, https://www.knackapp.com/
1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.
Credly, “How Credly Works,” https://info.credly.com/
Data for Democracy, “About Us,” https://www.datafordemocracy. org/about-us
Slack, https://get.slack.help/hc/en-us
Clare McGrane, “How 1,200 Volunteers on Slack Are Saving Democracy, One Data Set at a Time” in GeekWire (March 28, 2017) https://www.geekwire.com/2017/1200-volunteers-slack-saving-democracy-one-data-set-time/
Data for Democracy, “Featured Volunteers,” https://www. datafordemocracy.org/about-us
Data for Democracy, “About Us,” https://www.datafordemocracy. org/about-us
According to Engadget, as of May 2018, it had 135 million users, 19 million of whom used it every day, and 8.2 million people used it at the same time. Jon Fingas, “Discord Nearly Tripled Its User Base in One Year” in Engadget (May 15, 2018) https://www.engadget. com/2018/05/15/discord-user-base-nearly-triples-in-one-year/
u/AttaAtta, “Colony.io makes it easy for people all over the world to build companies together online.” in r/ethereum, Reddit (August
25, 2015) https://www.reddit.com/r/ethereum/comments/3ib76c/ colonyio_makes_it_easy_for_people_all_over_the/
Coin Interview, Episode 22, Colony.io with Jack du Rose and Aron Fischer. Streamed live on October 4, 2016. https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=H1D60pnFkNI
Etch, “Etch: The Payroll Platform to End Pay Day Loans” (October 2, 2017) https://pressreleases.responsesource.com/news/94073/ etch-the-payroll-platform-to-end-pay-day-loans/
Coin Interview, Episode 22, Colony.io with Jack du Rose and Aron Fischer. Streamed live on October 4, 2016. https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=H1D60pnFkNI
H. James Wilson, Paul R. Daugherty, and Nicola Morini-Bianzino, “The Jobs That Artificial Intelligence Will Create” MIT Sloan Management Review (March 23, 2017) https://shop.sloanreview. mit.edu/store/the-jobs-that-artificial-intelligence-will-create
H. James Wilson and Paul R. Daugherty, “Collaborative Intelligence: Humans and AI Are Joining Forces” in Harvard Business Review (July–August 2018) https://hbr.org/2018/07/collaborative-intelligence-humans-and-ai-are-joining-forces
Dennis R. Mortensen, “Automation May Take Our Jobs—But It’ll Restore Our Humanity” in Quartz (August 16, 2017) https://
qz.com/1054034/automation-may-take-our-jobs-but-itll-restore-our-humanity/
Steve Lohr, “‘The Beginning of a Wave’: A.I. Tiptoes Into the Workplace” in the New York Times (August 5, 2018) https://www. nytimes.com/2018/08/05/technology/workplace-ai.html
x.ai, https://x.ai/
The Center for Compassion and Altruism Research and Education, Stanford University School of Medicine, “About Compassion Cultivation Training (CCT),” http://ccare.stanford.edu/education/ about-compassion-cultivation-training-cct/
Peter Cappelli, Prasanna Tambe, and Valery Yakubovich, “Artificial Intelligence in Human Resources Management: Challenges and a Path Forward” (October 7, 2018). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn. com/abstract=3263878 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3263878
Dell Technologies “Digital Transformation Index,” conducted by Vanson Bourne, field work completed in August 2018: www. delltechnologies.com/DTIndex
Dell Technologies, “Gen Z is Here. Are You Ready?” Conducted by Dimensional Research, field work completed in September 2018: www.delltechnologies.com/GenZ
H. James Wilson, Paul R. Daugherty, and Nicola Morini-Bianzino, “The Jobs That Artificial Intelligence Will Create” MIT Sloan Management Review (March 23, 2017) https://shop.sloanreview. mit.edu/store/the-jobs-that-artificial-intelligence-will-create
Future of Work 15
0 notes
Text
Micron G9 NAND Takes Flagship Smartphones to The Next Level

Flagship smartphones need speedy and large storage to satisfy modern customers in a fast-paced, multitasking environment. An AI assistant in your pocket is becoming possible as AI technology progresses. AI is becoming agentic, allowing models to generate, reason, plan, and execute complicated multimodal tasks independently. Edge devices will need more memory and storage due to this transition.
Micron stated at MWC25 that UFS 4.1 and 3.1 would sample the first Micron G9 NAND for mobile devices. The latest NAND node, the G9 node, allows all storage options to achieve density and performance excellence.
Mobile UFS 4.1 G9 NAND
Micron G9 NAND mobile UFS 4.1 makes premium smartphones quicker and more responsive with its cutting-edge performance and innovation.
Faster speed and lower latency: Imagine quick language translation, faultless real-time photo editing, and a virtual assistant who knows you. AI-enabled apps driven by large language models (LLMs) are changing smartphone users' digital experiences. These services are expected to develop powerful multimodal AI agents that provide fast, complete, and contextual digital experiences. To achieve this, smartphones need fast access to massive datasets, lower latency, faster reaction times, and better end-user experiences.
Micron G9 NAND mobile UFS 4.1, with sequential read and write rates above 4100 MBps, leads this advancement. Compare G9 UFS 4.1 to G8 UFS 4.0 to see the performance gain.
Larger capacity: More storage allows for more local processing and computing capability. Traditional cloud-based AI systems process sensitive data via networks, increasing data breaches. Edge AI decreases risk by processing data locally, where it is produced. Micron's G9 UFS 4.1 offers 1TB NAND to boost on-device data processing and let your smartphone conduct complex calculations.
The smallest and thinnest package is the Micron G9 NAND UFS 4.1. Its capacity and ability to fit inside even the most innovative and sleek smartphone designs are equally significant. For next-generation foldable and ultra-slim smartphones, this space-saving design with the smallest 1TB NAND UFS package in the market at 9x13x 0.85mm1 allows for a bigger battery.
New proprietary features: Micron's firmware optimises data storage device placement and manner. These changes create a more responsive and efficient storage structure for AI use cases and smartphone performance improvement.
Smartphone delays often result from data defragmentation, which makes it harder for the device to read files. Micron's Data Defrag technology lets the UFS controller deliver defragmentation commands directly to the NAND, bypassing the host layer. By simplifying data migration, Data Defrag can boost smartphone read speeds by 60% for regular and AI activities. In conclusion, Data Defrag enhances read performance and reduces the device's strain by managing data relocation and fragmentation internally, allowing smartphones to retrieve information faster and smoother.
The CPU of a smartphone may "pin" frequently used data to the WriteBooster, a storage device, using Micron's technology. Dynamically loading relevant data from storage to memory is easier, ensuring speedier processing without consuming too much memory. Internal tests show this option increases random read speed by 30%.
The smartphone will run smoothly and launch applications and files faster using Pinned WriteBooster. This is useful for processing AI use cases and mobile use concurrently. The Pinned WriteBooster function creates a memory map for AI model data, speeding up data read and swap.
Micron Intelligent Latency Tracker (ILT) measures system and storage device I/O storage latency to discover and evaluate smartphone performance issues including slow app launching. By recognising latency issues, it helps smartphone OEMs optimise systems and improve user experience. This capability keeps smartphones running fast enough for AI apps and basic tasks like using the camera or finding a holiday photo in the gallery.
Zoned UFS (ZUFS): Imagine your bag nicely organised into shirts, trousers and socks before a vacation. This organisation helps you find things faster. Micron Zoned UFS (ZUFS) handles smartphone data similarly. ZUFS enhances read/write efficiency by grouping data with similar I/O characteristics into UFS device zones to reduce data search time. This streamlined data retrieval ensures faster and more smooth system functioning, like locating your well-packed socks in your luggage.
Faster intelligence: future-proofing innovations
Micron Mobile focusses on providing premium smartphones with cutting-edge NAND flash memory with unique characteristics. These advances accelerate edge AI applications. Working with customers and ecosystem partners, Micron is aligning its product and technology roadmaps with edge computing and AI advances. This cooperative technique ensures future mobile devices can handle data-intensive apps and more complicated AI. New firmware features and Micron G9 NAND demonstrate Micron's creativity.
#technology#technews#govindhtech#news#technologynews#Micron G9 NAND#G9 NAND#G9 NAND mobile UFS 4.1#Micron G9 NAND Flagship Smartphones#mobile UFS 4.1#G9 UFS 4.1
0 notes
Link
BERLIN–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Lenovo announced five new smart devices that unlock the power and
potential of intelligent technology today – using artificial
intelligence (AI), unleashing smart features and deploying augmented
(AR) and virtual reality (VR). With their affordable prices, these
devices make transformative technology accessible to mainstream
consumers and challenge the conventions of traditional category
boundaries. The Lenovo Mirage AR headset, Explorer Mixed Reality
headset, Moto X smartphone, Tab 4 Home Assistant and Yoga 920
convertible with special edition models bring you an unmatched number of
ways to enjoy a more personalized computing experience. Additionally,
the new 12-inch Yoga 720 convertible, Miix 520 detachable, both running
Windows 10® and ThinkVision P27u monitor extend the Lenovo
line of PC-related devices for even more choice.
VR/AR Bring Silver Screen Content to A Headset Near You – Premiers Star
Wars: Jedi Challenges
Star
Wars: Jedi Challenges is a new augmented reality Star Wars
product that allows fans to experience Star Wars in ways never
before possible. Jedi Challenges features a smartphone-powered Lenovo
Mirage AR headset, Tracking Beacon, Lightsaber controller, and hours of Star
Wars gameplay1. The product is compatible with both
Android phones and iPhones. Users start by downloading the Star Wars:
Jedi Challenges app2 onto their compatible phone and sliding
the phone into the tray of the Lenovo Mirage AR headset. Sleek, portable
and lightweight, the Lenovo Mirage AR headset will provide full gaming
immersion with an optimal level of comfort during gameplay. The headset
also comes with a Tracking Beacon, which is placed on the floor and acts
as a stable base for the headset’s sensors to detect the user’s movement
during gameplay. The headset pairs with a collectible-quality Lightsaber
controller modeled after the one wielded by Anakin Skywalker, Luke
Skywalker and Rey. Designed to be a key part of the experience, the
Lightsaber acts as a controller and pointer, allowing players to
navigate the user interface, with all controls, actions and commands
activated with a simple two-button configuration.
Our open approach to partnerships and building new experiences blending
devices and trailblazing content makes us different from other vendors,
and we think this approach leads to better, game-changing experience.
Together with Microsoft, we’re building a different type of VR world
with the Lenovo
Explorer Mixed Reality headset with more than 100 VR-ready titles.
We designed Lenovo Explorer as a natural, affordable extension of your
PC: You can access Microsoft Office suite, browse online or watch shows
in a virtual home office environment, play virtual reality (VR) games,
explore and discover through holo-tours, and enhance the video-watching
experience via 3D, 360-degree and 4K videos. Set it up in just minutes
by connecting a cable to your PC.
The Voice Service Goes Expressly Mobile – the New moto x4
Time to say ‘hello moto X’ once again. The fourth generation moto X has
a smarter camera that goes beyond capturing photos. The Landmark
Detection feature makes the moto X4 camera your eye to the
world – just point the lens at an object, and it will ask if you want to
learn about what you’re seeing. Or, spice up your selfies with the
Augmented Reality (AR) feature, which lets you add a layer of animations
to your photos or videos. The newest moto X4 is also the
first of Motorola’s smartphones to feature Amazon Alexa, giving you more
options when choosing a mobile digital assistant3. Experience
Amazon Alexa integrated right into moto x4 – without even
having to unlock it first. Now, whether you’re in a hotel, a friend’s
house or simply out and about, the features and benefits of Alexa are
always with you. The new moto x4: transforming smartphone
intelligence.
Transform Your Tablet – Lenovo Home Assistant Pack
Alexa makes other devices smarter too, and we’re bringing it first to
our tablets. The family-focused Tab 4 Series just got even more
versatile thanks to the Alexa-powered Home
Assistant Pack. Use your voice to get news, the weather or your
calendar, and see it all on the Tab 4’s display. Do even more with just
your voice, using it to shop online, listen to a song or control your
smart home. You can find what you’re searching for using the tablet’s
on-screen display cards on its 10-inch or 8-inch screen. All you need to
do is ask. The Home Assistant Pack equips the Tab 4 with the “Home
Assistant” app, a powerful three-watt speaker and far-field voice
detection with two mics so you can talk to search and hear your results
from up to three meters from any direction. To experience this level of
personalization, insert your Tab 4 into the Home Assistant Pack, watch
your screen switch to the Home Assistant Interface, and you’re ready to
go. And at just 320 grams, this lightweight tablet goes anywhere you do.
And with the optional Kid’s Pack and Productivity Pack, the Tab 4 now
lets you do a lot more, with one device. Besides offering the option to
transform into a smart assistant, the Tab 4 also offers a Kid’s Pack for
a 2-in-1 and a kid’s tablet and Productivity Pack to do more.
Personalizing the PC with Pen, Voice & Biometrics on Yoga 920
No longer does the PC stand for personal computing, characterized by
interaction happening in one-way exchange from person to device. Now PC
means personalized computing, and AI learning makes it contextually
aware of where you are. With this ability, your device can anticipate
your needs and interact with you in a variety of ways. The Yoga
920 convertible furthers the journey to a smarter laptop with new
smart pen functionality, voice recognition from a distance,4
mixed reality options,5 biometric security with Windows
Hello, and other tools.
Because many of us still want a keyboard or pen for creating, Yoga 920
offers an optional Lenovo Active Pen 2 great for Windows Ink

that has
4,096 levels of pen sensitivity for drawing and making notes with no
discernible lag. Additionally, voice recognition, a hallmark technology
of smartphones and smart speakers, comes to the Yoga 920 with Cortana.
Now it recognizes voice commands in standby mode and from up to 4 meters
away4 so you can add items to a shopping list, play music,
check the traffic, send a short email, track packages and much more.
Cortana even uses AI to learn from its owners, so the Yoga 920 grows
smarter over time. It fuses power, such as up to an 8th
Generation Intel® Core

i7 processor, Windows® 10 OS and
dazzling visuals with a nearly bezel-less 4K IPS touchscreen in a
13.9-inch frame.
Weighing in at just 1.37 kg (3.02 lbs), the four-mode convertible flexes
360° from a laptop into a tablet. Additionally, Yoga 920 comes in
limited edition Gorilla® Glass cover designs: Yoga
920 Vibes featuring a “visual vibration” design, Star Wars
Special Edition Yoga 920 Rebel Alliance and Star Wars Special
Edition Yoga 920 Galactic Empire.6
For those who want to see their laptop’s content on a larger screen,
they can pair it with the new ThinkVision P27u monitor. It has a 4K
borderless display, professional-grade color accuracy and fast response
times, with the convenience of USB Type-C connections and the
flexibility of a full function stand supporting an optional sound bar.
Additionally, we’re launching the 12-inch Yoga 720, our most portable
and compact Yoga 720 model yet at 0.62 inches thin and 2.53 pounds. It
comes equipped with optional Active Pen, fingerprint reader and Cortana
digital assistant. And the detachable Miix
520 with Windows 10 gives mobile users intuitive ways to create
content or immerse in entertainment with Lenovo digital pen, optional
WorldView camera for 3D imaging.
Pricing and Availability
Pricing and availability varies based on country. Check http://news.lenovo.com/IFA2017
for details.
1 For list of compatible smartphones, please visit
jedichallenges.com/compatibility. 2 Available at
jedichallenges.com/app. 3 Amazon Alexa integration is
available in markets where Amazon has Alexa, including the U.S., Germany
and UK. 4 Cortana with far-field voice-recognition
technology supports up to 4 meters away and in standby mode, requires
Windows 10 Fall Creators Update which will automatically update
automatically when it is available. 5 Mixed reality
requires Windows 10 Fall Creators Update which will automatically update
when it is available. Also requires purchase of a Lenovo Explorer
immersive headset for Windows Mixed Reality and Type-C to HDMI adapter. 6
Cover designs and color options may vary by geography and may only be
available in selected markets.
About Lenovo
Lenovo (SEHK:0992) (Pink Sheets:LNVGY) is a US$43 billion global Fortune
500 company and a leader in providing innovative consumer, commercial,
and enterprise technology. Our portfolio of high-quality, secure
products and services covers PCs (including the legendary Think and
multimode Yoga brands), workstations, servers, storage, smart TVs and a
family of mobile products like smartphones (including the Motorola
brand), tablets and apps. Join us on LinkedIn,
follow us on Facebook or
Twitter (@Lenovo)
or visit us at www.lenovo.com.

If you enjoyed this post, you should read this: Most women dont orgasm consistently, and it may be because they cant quiet their minds
from https://ift.tt/39Ifp17
0 notes
Text
AI year in review: Opportunities grow, but ethics loom large
VentureBeat is excited to announce VB Transform 2020, to be held July 15-16 in San Francisco, California. Register now for an early bird 40% discount.
Artificial intelligence garnered a lot of attention from the usual players — governments, tech giants, and academics — throughout 2019. But it was also a big year for business AI, with even more growth expected ahead. In a March KPMG survey, more than half of business executives said their company would implement enterprise-scale AI within two years. That is partly what drives PwC estimates that AI will deliver $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030.
Impressive leaps in 2019 have enabled new business applications for virtual assistants, such as Salesforce’s updated Einstein Voice Assistant for sales and customer service apps and IBM’s intelligent agent Watson Assistant. Meanwhile, governmental deployment of AI around the world has led to abuses and concomitant regulation. But along with concerns about power in AI comes the technology’s potential to help make everyday life a little better.
Automated AI for the enterprise
The enterprise cloud market heated up with increased implementation of automated machine learning (AutoML) that allows customers to apply AI to use cases such as marketing, customer service, and risk management. The biggest players in cloud computing — Google, Microsoft, and Amazon — spotlighted AI tools and automation in their annual tech showcases. Microsoft summed it up at Ignite 2019 with its tagline for Azure Cognitive Search: “Use AI to solve business problems.”
At the Google Cloud Next conference in April, Google announced new AutoML classes, premade Retail and Contact Center AI services, and the collaborative model-making tool AI Platform. In December, Amazon launched a blizzard of AI-powered enterprise tools at its re:Invent 2019 conference.
One of the more intriguing tools from Google Cloud Next was AutoML Natural Language, released widely in December, which analyzes text from a range of document and formatting types to feed sentiment analysis, legal document parsing, and publications management. Amazon rolled out a similar tool for AWS, called Textract, in April. Microsoft, meanwhile, pumped up the subject matter virtual agents, sentiment analysis, and business process automation available on its business-focused Power Platform.
AI at the edge
At the other end of the network — the edge — software advances like federated and multimodal learning are enabling artificial intelligence on smartphones and other devices, with the promise of greater control and better privacy protections compared to AI processed in the cloud. In June, Apple introduced Core ML 3, which allows iOS devices to perform machine learning for the first time. Google incorporated federated learning into its TensorFlow development environment back in 2017, and the effort is bearing fruit: In October, Google promoted the many AI touches on the Pixel 4 smartphone, from speech recognition to greatly improved camera features.
Hardware is also becoming more efficient, with “real AI” powered by mobile chips. Examples abound: Arm is building up its product line to power machine learning and AI in a wide selection of devices. Intel promoted Keem Bay, a vision processing unit that brings inferencing tasks to edge devices. Google offered Coral AI, a range of boards and kits for neural network machine learning that work on the edge. And Nvidia released the Jetson Xavier NX to power AI for drones, cars, and other mobile edge devices.
In addition, a new focus on power efficiency could help reduce the environmental (and financial) impact of running all those AI systems. Google created a controller that keeps its experimental quantum processor cool enough to function while using just 2 milliwatts of power. On the consumer side, Facebook announced DeepFovea, an AI technique that improves the power draw of VR headsets. And even closer to home, Sense released a line of AI devices to monitor and reduce household energy use, while Evolve Energy’s AI helps solar and wind power customers find the best prices and save energy.
Shipping and shopping
Besides consumer energy monitors like the above, 2019 saw huge advances in areas like autonomous cars and the internet of things (IoT). AI also made inroads into such everyday tasks as grocery shopping.
Self-driving cars from the likes of Uber, Lyft, Alphabet’s Waymo, Tesla, and Argo are the pretty face of autonomous vehicles, and consumer sentiment reports suggest the public is warming to the idea. But commercial trucking was where the money was in 2019. Carmaker Volvo is so confident in the viability of its smart trucks that it’s going to break out its driverless financials starting in 2020, although it faces competition from the likes of TuSimple, which is testing delivery for the U.S. Postal Service; Daimler, which is testing autonomous trucks in Virginia; and Starsky Robotics, which relies on remote teleoperators to run its test fleet.
Competition in the AI assistant market is still greatest between Amazon and Google, rivalry that has spurred the performance and capabilities of voice recognition and personal assistants. Amazon and Microsoft launched the Voice Interoperability Initiative in September, along with a slew of partners — absent Apple, Samsung, and Google — that seek to allow devices to run more than one assistant. There’s good reason for Microsoft to join, since it’s become clear its Cortana is not beating Amazon’s Alexa or Google Assistant anytime soon. But Samsung’s Bixby also stepped back in acknowledgment of its market position. As for which voice assistant is best, Google Assistant keeps coming out on top in accuracy tests, although in a May 2019 test by Tom’s Hardware, Alexa and Siri were not far behind.
AI went mainstream for grocery shopping in 2019. Walmart is using AI to improve online grocery ordering, employing machine intelligence to figure out what consumers are likely to need, and it’s begun using driverless vans to ferry goods between stores in Arkansas. Meanwhile, Microsoft helped grocery chain Kroger create cashierless stores using smart shelves and other intelligent technology, while the Giant Eagle chain turned to Grabango for its own AI trial.
Governmental give-and-take
Politicians and corporations clashed throughout 2019 over the appropriate use and oversight of AI. Famously, one of Democratic senator and presidential candidate Elizabeth Warren’s campaign promises is to break up big tech businesses like Google and Amazon. “With fewer competitors entering the market, the big tech companies do not have to compete as aggressively in key areas like protecting our privacy,” Warren’s campaign blog states. And her rivals brought up AI specifically in the Democratic debates.
Beyond the general concern of private-market encroachments upon personal freedoms, governments from the Massachusetts town of Somerville to the nation of the U.K. are examining how the public sector should use AI technology — and coming to differing conclusions.
While China has been using facial recognition to regulate cell phone accounts and allegedly round up the Uighur minority population, most governments in the U.S. that examine the technology do so to limit or ban its use. Especially in California, San Francisco and other cities are enacting bans on use of facial recognition by public entities, particularly police departments.
Detroit has no such ban, and indeed its police chief, James Craig, is enthusiastic about facial recognition’s potential to fight crime. This led to an August 2019 Twitter beef for the ages between Chief Craig and Detroit’s U.S. Congressional Representative, Rashida Tlaib (D-MI), that ended in an awkward demonstration of the technology that frustrated both sides.
The tide could turn if President Trump wins re-election in 2020, as his administration takes a more collaborative approach to AI. If the eventual Democratic nominee is Senator Bernie Sanders (D-VT), and he wins, Chief Craig might be out of luck. But legislation to regulate facial recognition has been surprisingly nonpartisan so far.
Smart cities
Despite privacy concerns over government use of AI, the technology can improve everyday life, especially if proper care is taken to consider the ethics.
The amount of data being created by smart cars, roadside cameras, public transit, and other sensors is overwhelming, but by feeding it into AI systems, companies like Waycare are helping cities predict and improve traffic flow. StreetLight Data takes a different approach: By tapping into cellphone location data, it can track and predict traffic for vehicles, bicycles, and pedestrians. London is using Waze to tackle traffic congestion in the city center and reduce air pollution. Elsewhere, Alphabet division Sidewalk Labs is helping Toronto push the envelope of smart city technology, fed by weather and usage patterns, to create a high-tech innovation district.
Norway has emerged as a hotbed for startups leveraging AI to build better cities. Oslo-based Spacemaker‘s software allows city planners to estimate the effect of each planning decision and optimize for a range of goals, courtesy of machine learning. And in August, the city of Trondheim unveiled Powerhouse, a smart office building designed to generate more energy than it consumes and apply the excess to powering other smart city tech, such as road monitoring.
As 2019’s projects come to fruition in 2020 and beyond, it will be interesting to watch how AI develops in the real world. Ethical oversight will be needed to make sure the technology continues to serve humanity, rather than the other way around.
Join us at VB Transform 2020, the AI event of the year for enterprise executives, brought to you by today’s leading AI publisher. You can purchase tickets below.
The post AI year in review: Opportunities grow, but ethics loom large appeared first on Actu Trends.
0 notes